API Security for Visa Platforms: mTLS, Key Rotation, and Least‑Privilege Design

APIs that handle passport data, biometric scans, and payment details sit squarely in the cross-hairs of fraudsters and state-sponsored actors alike. When that API is the backbone of a visa-processing platform, any breach can halt airline operations, trigger fines for denied boardings, and erode traveller trust overnight. That is why the most forward-thinking travel brands now evaluate security controls with the same scrutiny they apply to uptime SLAs or conversion metrics.
In this guide we break down three pillars of a hardened visa API: mutual TLS (mTLS), automated key rotation, and least-privilege design. We will show how these measures work together, where they often fail in the wild, and the practical steps you can take—whether you build in-house or select a provider like SimpleVisa—to keep sensitive travel data safe.
Why Visa APIs Are High-Value Targets
- Rich data payloads: Visa submissions combine PII, payment info, and sometimes biometric files—everything an attacker needs for identity fraud.
- Strict regulatory oversight: Airlines face carrier-liability fines up to six figures per passenger if invalid documents slip through. A compromised API can propagate bad data at scale.
- Real-time decision windows: Fraudulent calls that saturate endpoints during a boarding window can delay flights and tarnish customer experience.
For these reasons, travel sellers and border agencies increasingly insist on verifiable, defense-in-depth architectures—and they start by looking at the TLS handshake itself.
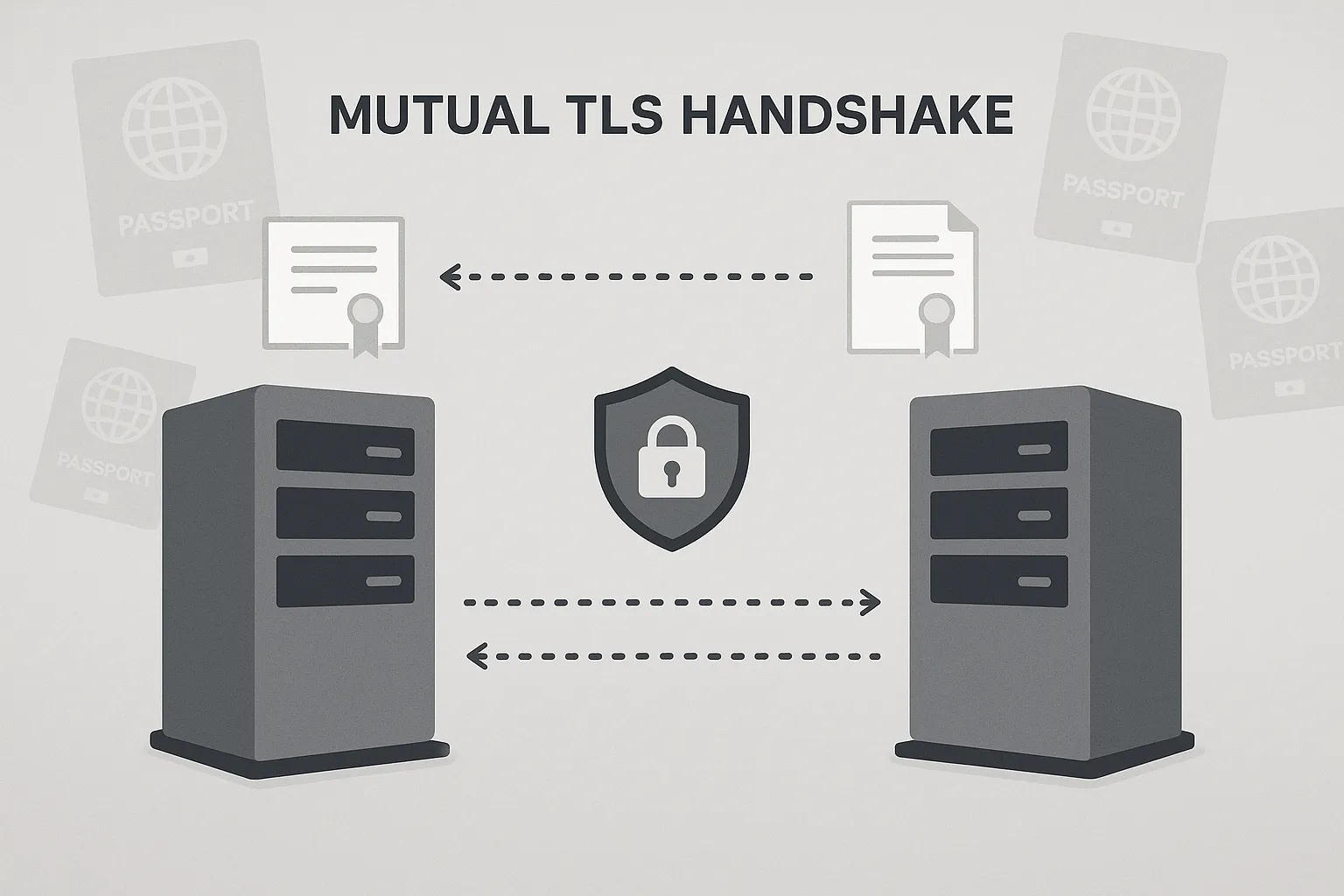
1. Mutual TLS: Authenticating Both Client and Server
Most APIs rely on one-way TLS: the client validates the server certificate, then sends a bearer token. mTLS adds the missing half of the handshake. The client must also present a X.509 certificate signed by a trusted CA, turning every request into a cryptographically proven identity exchange.
1.1 How the mTLS Handshake Works
| Step | Client action | Server action | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Initiate TLS ClientHello | Respond with ServerHello and server cert | Server proves identity |
| 2 | Send client certificate | Validate against CA chain and revocation list | Client proves identity |
| 3 | Exchange ephemeral keys | Complete TLS setup | Encrypted channel established |
| 4 | Attach JWT or API call | Verify application-layer auth (optional) | Request processed |
Key takeaways:
- Even if a token leaks, an attacker still needs the private key for the certificate to gain access.
- Certificate revocation gives ops teams a kill switch during an incident.
1.2 Production Pitfalls and Fixes
- Wildcard trust stores: Allowing any CA-signed certificate defeats the purpose. Pin your own intermediate CA or use short-lived client certs issued by a dedicated PKI.
- Lack of rotation strategy: Expired client certs can trigger outage cascades. Automate re-issue at least 10 days before expiry and alert on failures.
- Mobile or browser clients: If you expose mTLS to end users, store keys in the device secure enclave and enable remote wipe for lost devices.
SimpleVisa enforces mTLS on all server-to-server calls—including eligibility lookups, application submission, and webhook delivery—and provides a helper CLI that generates client certificates signed by our private CA in seconds. You can review the exact steps in our Developer Q&A: Best Practices for Authenticating Against the SimpleVisa API.
2. Key Rotation: Secrets That Never Gather Dust
Hard-coded API keys and decade-long certificates live on borrowed time. According to Verizon’s 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report, 61 percent of API incidents traced back to compromised or reused credentials. Regular rotation limits the blast radius of a leaked secret and satisfies compliance frameworks such as ISO 27001, PCI DSS, and GDPR.
2.1 Rotation Cadence and Triggers
- Time-based: Rotate every 60-90 days. Shorter windows for high-risk environments.
- Event-based: Rotate immediately after employee off-boarding, code repo leak, or penetration-test finding.
- Certificate-expiry: Automate renewal at 80 percent of certificate lifespan.
2.2 Rolling vs Hard Cut-over
| Pattern | Pros | Cons | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rolling dual-key | Zero downtime, graceful failover | Slight code complexity | Multi-tenant SaaS, airlines with 24-7 traffic |
| Hard cut-over | Simpler logic | Possible minutes of downtime | Low-volume back-office tools |
SimpleVisa uses rolling dual-key rotation behind the scenes. During the overlap window both the old and new keys remain valid, so live bookings keep flowing. Partners receive webhook alerts and an API endpoint to confirm the new fingerprint programmatically.
2.3 Tooling Recommendations
- Store secrets in a vault (AWS Secrets Manager, HashiCorp Vault, GCP Secret Manager).
- Use short-lived, scoped JWTs exchanged for long-lived client-certs so that frontend code never sees raw API keys.
- Monitor usage analytics for calls signed with deprecated keys—spikes often signal scraping or credential stuffing.
For a hands-on example, the Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Sandbox eVisa Transactions shows how rotation works in a controlled environment.
3. Least-Privilege Design: Because “Read Only” Should Mean Read Only
Giving every integration ‘admin’ scopes is convenient—until someone scripts a mass-delete or attackers escalate privileges. Least-privilege design limits each token, role, and microservice to the minimum actions and data fields required.
3.1 Scope Granularity in Visa Workflows
| Role / Use Case | Sample Allowed Actions | Sample Denied Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility gadget on flight-search page | GET /eligibility |
POST /application, GET /pdf |
| Payment microservice | POST /payment-intents |
GET /passport-scan |
| Support dashboard | GET /application, PATCH /application.status |
DELETE /application |
Implement scopes at three layers:
- API gateway: JWT claims checked on every request.
- Service mesh: Sidecar proxies enforce mTLS and destination policies.
- Data store: Row-level security to prevent broken-object-level authorization (BOLA) attacks flagged by OWASP.
3.2 Data Minimization
Visa forms typically ask for dozens of fields. Yet most resellers only need two: approval status and expiry date. Mask, redact, or tokenise everything else before it hits your logs or analytics pipeline.
SimpleVisa’s GET /application endpoint supports a fields= parameter so you can request the exact attributes you need—nothing more. Combined with per-scope response filtering, this slashes your GDPR exposure footprint.
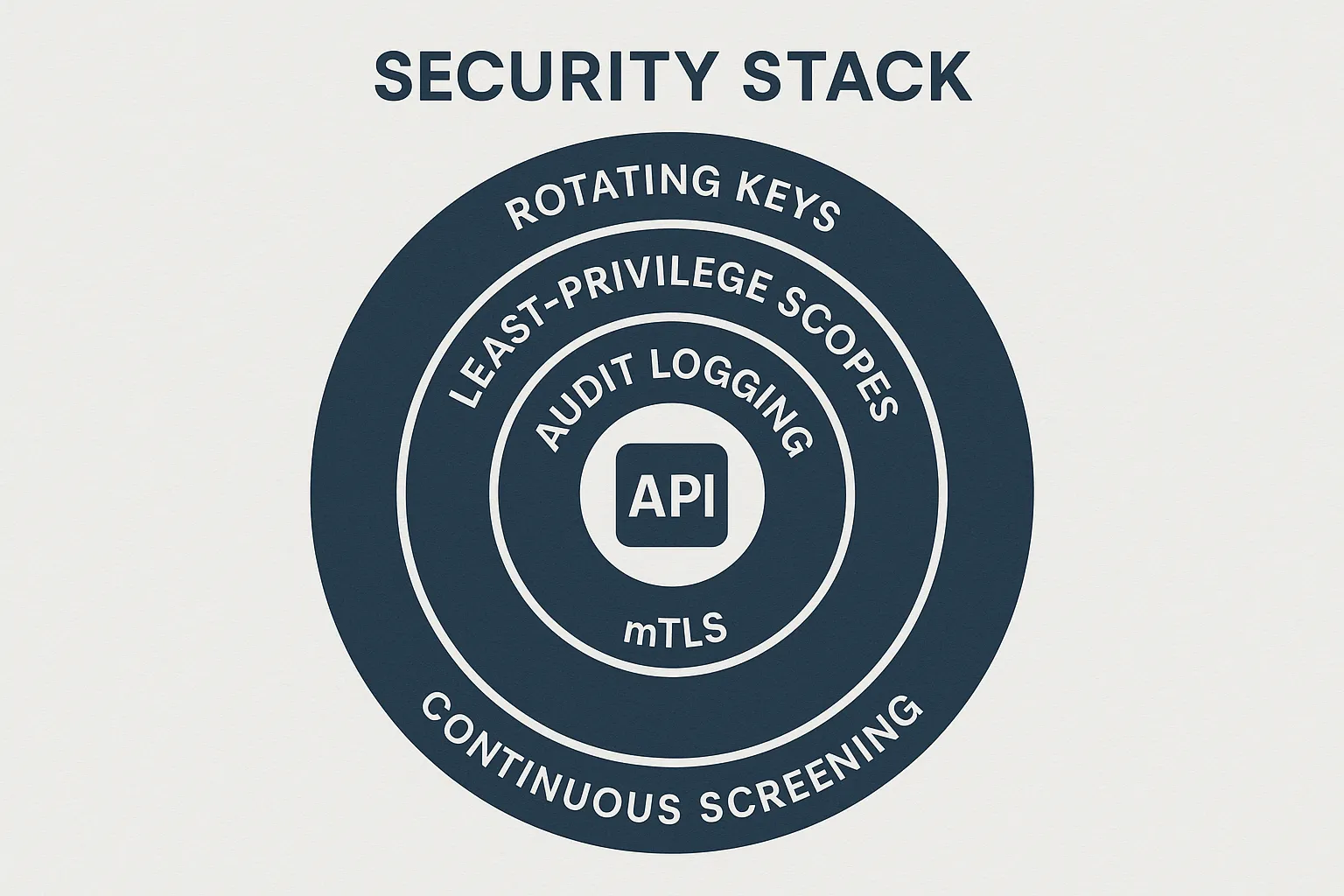
4. Building Defense in Depth for Border-Crossing APIs
A secure handshake, fresh keys, and tight scopes are necessary but not sufficient. Complete your stack with the following controls:
- Continuous watch-list screening: Check every change event against INTERPOL and EU Sanctions data in real time.
- Immutable audit logs: Ship cryptographically signed events to append-only storage like Amazon S3 Object Lock.
- Threat-aware rate limiting: Burst-aware algorithms that distinguish legitimate batched submissions from brute-force attacks.
- Zero-trust network zones: Segregate prod, staging, and sandbox VPCs; block east-west traffic by default.
- Certified hosting: ISO 27001 and SOC 2 audits with annual penetration tests.
For a broader checklist see Top 8 Security Features to Demand in Any Electronic Visa Solution.
5. Quick Vendor Evaluation Checklist
Ask every visa-technology provider—or your own engineering team—these five questions:
- Do you enforce mTLS on every server-to-server call, including webhooks?
- What is the maximum lifetime of an API key or client certificate?
- Can roles be scoped to single endpoints and even specific response fields?
- How do you cryptographically sign and store audit logs for five-plus years?
- Which third-party labs performed the last penetration test, and can we see the executive summary?
If any answer is vague or postponed to “phase two”, keep looking.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need mTLS if my API already uses OAuth2? Yes. OAuth2 handles authorization but still relies on the underlying transport layer. mTLS blocks man-in-the-middle attacks that target token exchange.
How often should I rotate client certificates? Industry guidance from NIST SP 800-57 suggests 90 days or less for high-sensitivity data. Many SimpleVisa partners opt for 60-day cycles to align with sprint cadences.
Can least-privilege slow down development? Properly implemented scopes are additive—developers request the minimal permissions and receive them in minutes. Over time you save debugging hours by isolating risky calls.
Secure Your Visa Flow in Days, Not Months
Hundreds of travel brands rely on SimpleVisa’s API and white-label tools to automate border-crossing compliance while meeting strict security benchmarks. If you want to see how mTLS, key rotation, and least-privilege design are baked into our stack—and how quickly you can launch a compliant visa upsell—schedule a 30-minute security deep-dive with our solutions team.
Protect passenger data, avoid carrier-liability fines, and unlock new ancillary revenue streams—all with enterprise-grade security by default.
Ready to start? Book your demo here.