Online Visa Processing: How It Works Behind the Scenes

If you have ever clicked Apply on an online visa form and received an approval within hours, it looks simple on the surface. Behind the scenes, modern online visa processing is a tightly orchestrated pipeline of rule engines, identity checks, fraud screening, secure submissions to government portals, payments, and real‑time status handling. This article lifts the hood on that pipeline so travel teams and curious travelers understand what actually happens after you press submit.
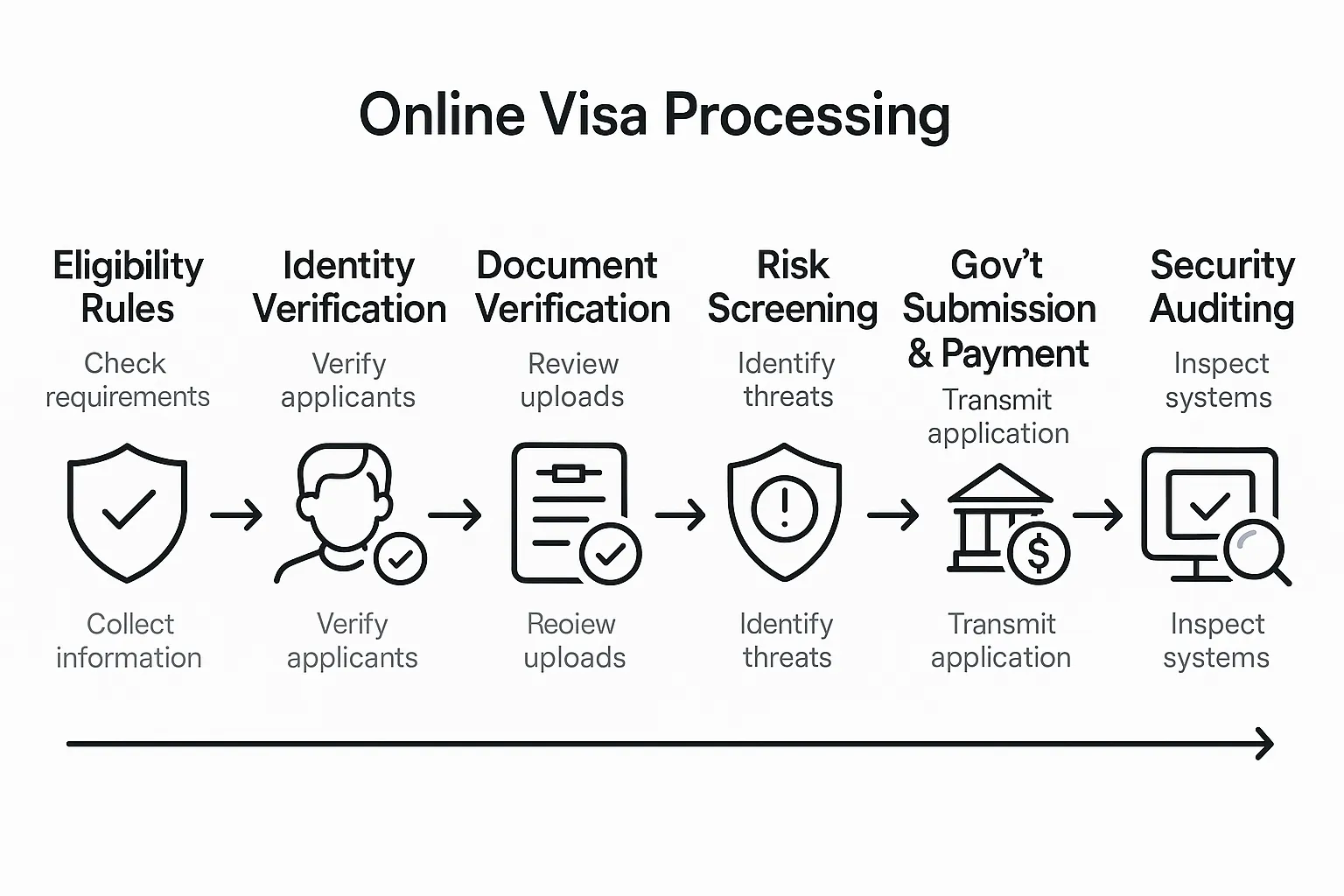
Why online visa processing is more than a web form
Online visa processing is a system of systems. A typical journey includes:
- Eligibility intelligence, a rules engine maps your nationality, destination, and trip purpose to the correct authorization.
- Dynamic experience, the form adapts to your answers and only requests the documents that apply to you.
- Identity verification, the platform validates your passport data, photo, and sometimes your biometric liveness.
- Risk and compliance, automated checks verify sanctions exclusions, duplicate applications, and fraud signals.
- Government handoff, your application is transformed into the exact schema and submitted via an API or secure portal, fees are reconciled.
- Tracking and exceptions, statuses, requests for more information, and approvals are synchronized across channels.
- Security and governance, data is encrypted, access is role based, and a full audit trail is kept for regulators.
For context, most countries now support some mix of eVisa or eTA for short stays. Programs like the EU’s upcoming ETIAS are expanding digital pre‑screening, see the official European Commission ETIAS portal. Standards such as ICAO Doc 9303 for machine readable travel documents and NIST’s Digital Identity Guidelines inform how identity is captured and verified online.
The seven layers behind online visa processing
1) Requirement intelligence, the rules engine
Everything starts with accurate rules. Platforms ingest official government notices, airport and airline advisory feeds, and treaty changes, then normalize them into machine readable logic. A typical engine evaluates:
- Nationality and passport attributes, validity, blank pages, previous visas
- Itinerary details, destination, transits, entry points, dates
- Purpose of travel and supporting proofs, tourism, business meetings, study, medical
- Special programs, visa exemptions, eTA eligibility, reciprocity conditions
Outputs include the correct document type, required fields and evidence, fees, expected processing times, and whether an interview or biometrics will be requested.
Further reading, What Is Travel Document Automation?
2) Dynamic form orchestration and UX
Modern platforms do not show a one size fits all questionnaire. Instead, they build a personalized flow in real time. Common patterns include progressive disclosure, contextual help in plain language, automatic unit conversions, address and employer lookup, real time validation and deduplication.
Documents are requested only when needed, with capture helpers, camera based passport scanning, auto crop, glare and blur detection, and instant feedback on photo requirements. This approach reduces abandonment and errors. See the UX playbook in Why Travelers Abandon Visa Forms, and 6 UX Fixes That Convert.
3) Identity capture and document verification
Once data is entered, the system validates that you are who you say you are.
- MRZ and NFC parsing, passport MRZ is read and checked for checksums that match [ICAO 9303] formats. Some systems can read the ePassport chip on compatible phones to cross check identity data.
- Photo and liveness checks, face images are checked against ICAO and ISO specifications for size, background, and contrast. Optional liveness prompts, blinking or motion, reduce spoofing.
- Document authenticity signals, font and layout checks, EXIF anomalies, tamper detection, and cross field consistency.
The outcome is a confidence score that determines if the application proceeds automatically or gets flagged for manual review.
Deep dive, 4 Technologies Behind the Electronic Visa System
4) Risk, watchlists, and compliance
Visa platforms run layered screening before any government submission. Typical checks include sanctions and watchlist comparisons, politically exposed person detection, known fraud patterns like repeated attempts from the same device with different identities, impossible itineraries or document inconsistencies, IP and device reputation, and geolocation mismatches.
High risk signals can trigger additional evidence requests, a manual review queue, or a decision not to submit.
5) Government submission, payment, and reconciliation
This is where behind the scenes complexity spikes, since every government has its own schema, portal flow, payment method, and session handling.
- Schema mapping and validation, fields are transformed to the exact format and language required by the issuing authority. Required attachments are resized and converted to accepted formats.
- Transport to government systems, direct APIs where available, headless browser sessions where APIs are not provided, secure file exchanges for bulk submissions in some programs.
- Fee payment and receipts, government fees are paid through approved gateways, receipts are captured, and reconciliation is logged to match charges with specific cases.
- Idempotency and retries, duplicate submissions are prevented with idempotency keys, transient errors trigger controlled retries, and long running jobs are queued.
For a step by step government handoff walkthrough, see How eVisa APIs Work.
6) Status tracking, notifications, and exceptions
After submission, your application moves through statuses. The platform polls or receives webhooks and keeps applicants and partner systems updated in plain language.
| Status label you see | What is happening behind the scenes | Typical next action |
|---|---|---|
| Received | Government system accepted payload and created a case ID | Wait for screening to start |
| In review | Automated screens passed, officer review pending | No action unless contacted |
| Additional info requested | Evidence or a corrected document is needed | Upload the requested item by the deadline |
| Approved | Authorization issued and linked to your passport | Save the PDF or reference, travel within validity |
| Refused | Decision issued, with reason codes | Consider re application or alternate route |
| Expired | Authorization is no longer valid | Apply for a new authorization |
Exceptions are normal. A robust platform supports editable resubmissions with audit continuity, deadline reminders, secure messaging threads that attach to the case, and escalation paths when travel is imminent.
7) Security, privacy, and audits
Online visa platforms handle sensitive identity data, so the bar is high.
- Data minimization and encryption, only essential fields are collected, data is encrypted in transit and at rest, and secrets are rotated regularly.
- Access controls and logging, strict role based access, short lived session tokens, immutable audit logs.
- Retention and deletion, data is retained only as long as required by law or contractual obligations, then purged with verifiable deletion.
- Compliance posture, alignment with frameworks like GDPR and expectations for ISO 27001 type controls. Government audits and partner assessments are common in this category.
For developers integrating platforms, best practices on authentication and key management are covered in Developer Q&A: Authenticating Against the SimpleVisa API.
A quick view of the pipeline
| Layer | Purpose | Key checks | Failure modes to plan for | What good looks like |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Requirement intelligence | Decide eligibility and required evidence | Nationality rules, transit, purpose, reciprocity | Outdated rules, edge case itineraries | Rules updated daily, test coverage on tricky cases |
| Dynamic forms | Collect only what is needed | Conditional logic, inline validation | Form abandonment, missing documents | Sub 10 minute completion for simple cases |
| Identity verification | Prove who is applying | MRZ checks, photo specs, liveness | Blurry scans, tampered images | Automated pass rate above 90 percent with manual fallback |
| Risk screening | Reduce fraud and rejections | Watchlists, device reputation | False positives, latency | Tuned thresholds and clear appeal flow |
| Submission and payment | Move data to the authority | Schema mapping, payment reconciliation | Session timeouts, duplicate charges | Idempotent submissions and resilient retries |
| Tracking and exceptions | Keep everyone informed | Webhooks, SMS or email alerts | Missed deadlines, silent failures | Clear statuses and deadline timers everywhere |
| Security and audits | Protect data and trust | Encryption, RBAC, deletion workflows | Unauthorized access, data retention drift | Third party audits and live runbooks |
What travelers see vs what the system does
- You pick tourist or business, behind the scenes, the engine maps you to the correct program, prompts for the right evidence, and calculates fees.
- You upload a passport photo, the system checks resolution, background, head ratio, and glare, and prompts you to retake if needed, which avoids rejections later.
- You get an approval email, on the backend, a webhook from the authority updated the case, a PDF was stored, and your record was linked to the booking so airline check in systems can verify it.
How travel brands plug online visa processing into their journey
Travel sellers have three common integration paths, each with different time to market and control.
- No code widget, fastest route, embed a drop in module on checkout or post booking pages. See the Quick Tutorial: Embedding an eVisa Widget.
- White label portal, launch a branded visa center that you can link from confirmation emails or your help center.
- Direct API, maximum control, surface eligibility and the full application in your native flow. Compare options in API vs. White Label App.
SimpleVisa supports all three models, including visa processing automation, a white label app, custom data services, and a no code option. The service is already live on 400 plus partner sites, helping brands guide customers through border requirements while unlocking ancillary revenue.
What to measure once you deploy
Operational excellence is measurable. Teams typically track the following KPIs:
- Visa related conversion rate, of eligible bookings, how many start and complete an application
- Ancillary revenue per booking, revenue uplift from visa and related add ons
- Application completion time, average minutes to complete by visa type
- Approval rate, approvals divided by decisions, with breakdowns by nationality and program
- Customer satisfaction and support load, NPS or CSAT and tickets per 1,000 bookings
For definitions, benchmarks, and a dashboard blueprint, see 5 KPIs to Track After Deploying a Visa Management Platform.
Common misconceptions, clarified
- Instant equals automatic, some authorizations are near instant for low risk travelers, others take hours or days and may involve human review. A good platform sets realistic timelines.
- Printing is always unnecessary, many borders accept fully digital checks, some still recommend or require a printed copy as a fallback. Your provider should advise per destination.
- Approval guarantees entry, final admission is always at the discretion of border officers. Platforms help reduce risk, they cannot guarantee entry.
If you need a primer on security and fraud, this overview of Electronic Visa Scams and How to Avoid Them is a useful companion.
What is changing in 2025 and beyond
- Pre travel screening becomes the default, programs like ETIAS in Europe and expanded ETAs in the UK move more checks upstream before departure.
- Better interoperability, authorities are gradually adopting standardized schemas and machine readable outcomes, which reduces error rates.
- Stronger identity, biometric liveness and chip reading on consumer devices are becoming more common, guided by standards like ICAO 9303 and NIST 800 63.
- Embedded experiences, eligibility, pricing, and full online visa processing increasingly appear natively inside flight and tour bookings.
For a broader look at technology trends, see Future of Travel APIs: From Flights to Visas in a Single Call.
Bringing it all together
Online visa processing is a coordinated stack of rules, identity, risk, payments, and secure data handling. Travelers feel the benefits as fewer surprises and faster approvals. Travel brands see higher conversion, fewer denied boardings, and new ancillary revenue.
If you want to add online visa processing to your booking flow without months of engineering, SimpleVisa offers API integration, a white label app, and a no code implementation option. You can guide customers through border requirements and unlock new revenue, all with a high approval rate and premium eVisa management. To see it in action, request a demo. You can be live in days, not months.
Further resources
- How eVisa APIs Work, Step by Step
- 4 Technologies Behind the Electronic Visa System
- API vs. White Label App
- 5 KPIs to Track After Deploying a Visa Management Platform
- IATA’s overview of travel requirement data feeds, Timatic